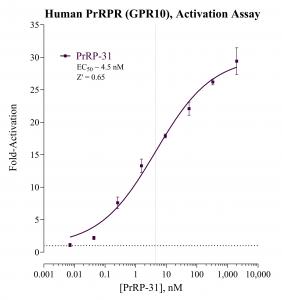
INDIGO Biosciences Launches PrRPR/GPR10 Reporter Assay for Metabolic, Neuroendocrine, and Cardiometabolic Research
New Cell-Based Assay Supports Drug Discovery Targeting Appetite Regulation, Stress Biology, and Autonomic Function
STATE COLLEGE, PA, UNITED STATES, February 19, 2026 /EINPresswire.com/ -- INDIGO Biosciences, a premier provider of cell-based reporter assay solutions, has announced the launch of its Human Prolactin-Releasing Peptide Receptor (PrRPR/GPR10) Reporter Assay. This new assay provides researchers with a robust, ready-to-use platform for studying PrRPR signaling and accelerating therapeutic discovery in metabolic disease, neuroendocrine disorders, stress biology, and cardiometabolic research.“The prolactin-releasing peptide receptor sits at a critical intersection of appetite regulation, stress response, and autonomic signaling,” said Dr. Andrew Woodman, Lab Director at INDIGO Biosciences. “By introducing a functional reporter assay for PrRPR, INDIGO enables scientists to better understand receptor pharmacology and generate high-quality data that support emerging therapeutic strategies across multiple disease areas.”
PrRPR, also known as GPR10, is a class A G protein-coupled receptor activated by prolactin-releasing peptide (PrRP). The receptor is expressed in hypothalamic and brainstem regions that regulate energy balance, neuroendocrine signaling, and autonomic cardiovascular control. Activation of PrRPR has been shown to influence feeding behavior, metabolic homeostasis, hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis activity, and sympathetic nervous system function, positioning it as a relevant target for obesity, stress-related conditions, neuropsychiatric research, and neuro-cardiometabolic disease mechanisms.
“INDIGO is committed to delivering tools that simplify complex workflows while producing reliable, reproducible data,” added Woodman. “The launch of the PrRPR/GPR10 Reporter Assay expands our growing portfolio of GPCR and neuroendocrine receptor assays and provides researchers with an accessible solution for screening ligands, evaluating receptor activity, and advancing next-generation metabolic and CNS therapeutics.”
INDIGO’s PrRPR/GPR10 Reporter Assay kit includes all materials required to perform the assay, including cryopreserved, optimized reporter cells, media for cell recovery and compound dilution, a validated reference agonist, luciferase detection reagents, cell culture-ready assay plates, and detailed protocols. INDIGO’s Human PrRPR/GPR10 Reporter Assay is available as an all-inclusive kit in 96-well and 3×32-well formats, with bulk reagent options available to support high-throughput screening programs.
What sets INDIGO’s assay kits apart is their proprietary CryoMite™ cryo-preservation process. This innovative technology eliminates the need for weeks of cell culture work, allowing researchers to immediately dispense healthy, division-competent reporter cells into assay-ready plates. The process streamlines the workflow, requiring no intermediate steps such as cell rinsing, viability checks, or titer adjustments. Researchers simply thaw the cells, plate them, add test compounds and detection reagents, and obtain results in as little as 24 hours.
Researchers may also outsource PrRPR studies through INDIGO’s assay services, offering a convenient and cost-effective alternative to in-house testing while ensuring access to high-quality, reproducible data backed by INDIGO’s assay expertise.
Michael Gardner
INDIGO Biosciences, Inc.
+1 814-234-1919
email us here
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.